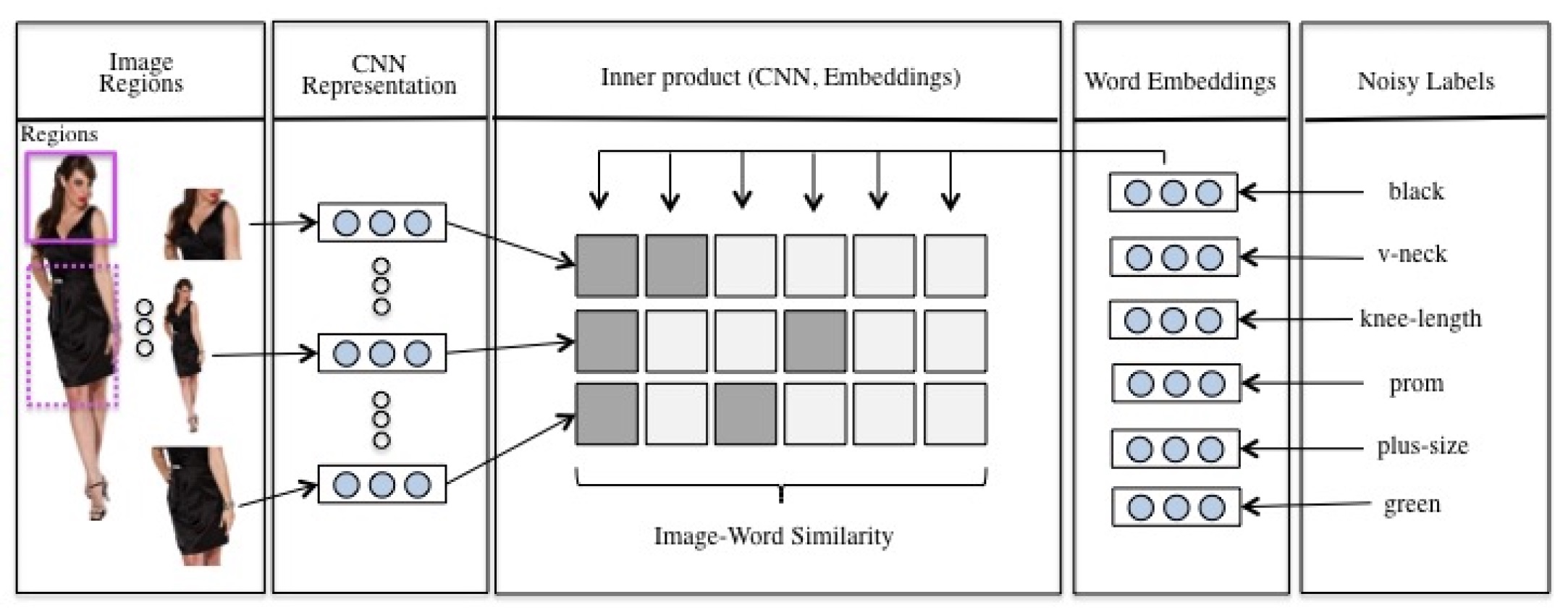
Cross-modal Search for Fashion Attributes
In this paper we develop a neural network which learns inter- modal representations for fashion attributes to be utilized in a cross-modal search tool. Our neural network learns from organic e-commerce data, which is characterized by clean image material, but noisy and incomplete product descrip- tions. First, we experiment with techniques to segment e- commerce images and their product descriptions into respec- tively image and text fragments denoting fashion attributes. Here, we propose a rule-based image segmentation approach which exploits the cleanness of e-commerce images. Next, we design an objective function which encourages our model to induce a common embedding space where a semantically related image fragment and text fragment have a high in- ner product. This objective function incorporates similarity information of image fragments to obtain better intermodal representations. A key insight is that similar looking image fragments should be described with the same text fragments. We explicitly require this in our objective function, and as such recover information which was lost due to noise and in- completeness in the product descriptions. We evaluate the inferred intermodal representations in cross-modal search. We demonstrate that the neural network model trained with our objective function on image fragments acquired with our rule-based segmentation approach improves the results of image search with textual queries by 198% for recall@1 and by 181% for recall@5 compared to results obtained by a state-of-the-art image search system on the same benchmark dataset.
Check out our paper
Cross-modal Search for Fashion Attributes
KDD Machine Learning Meets Fashion Workshop, 2017
Katrien Laenen, Susana Zoghbi, Sien Moens
You May Also Like
Latent Dirichlet Allocation for Linking User-Generated Content and e-Commerce Data
Automatic linking of online content improves navigation possibilities for end users. We focus on linking content generated by users to other relevant sites. In particular, we study the problem of linking information between different usages of the same language, e.g., colloquial and formal idioms or the language of consumers versus the language of sellers. The challenge is that the same items are described using very distinct vocabularies. As a case study, we investigate a new task of linking …
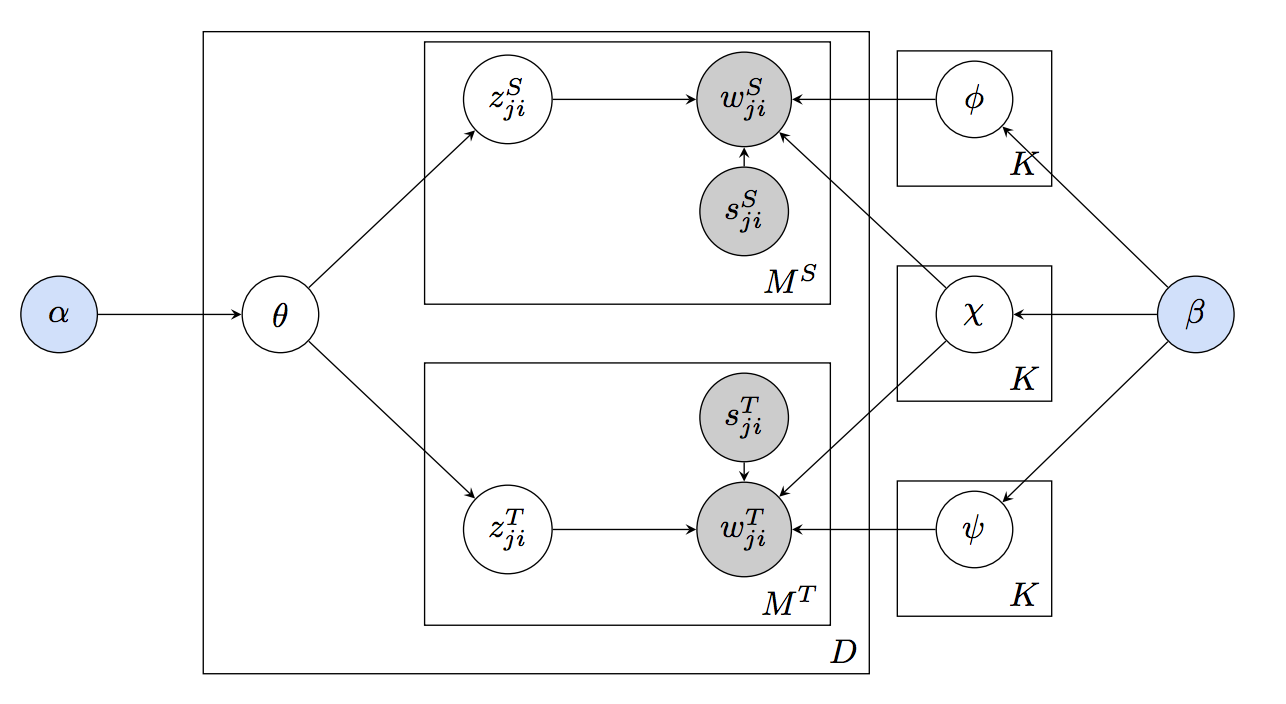
Learning to Bridge Colloquial and Formal Language Applied to Linking and Search of E-Commerce Data
We study the problem of linking information between different idiomatic usages of the same language, for example, colloquial and formal language. We propose a novel probabilistic topic model called multi-idiomatic LDA (MiLDA). Its modeling principles follow the intuition that certain words are shared between two idioms of the same language, while other words are non-shared. We demonstrate the ability of our model to learn relations between cross-idiomatic topics in a dataset containing product …
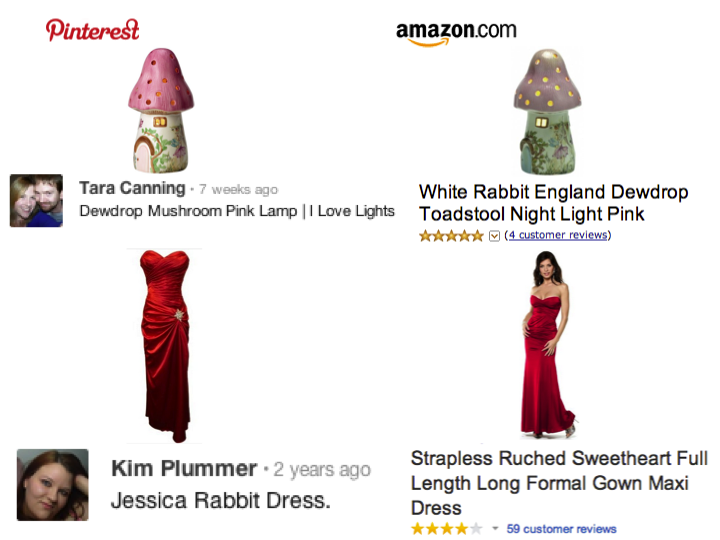
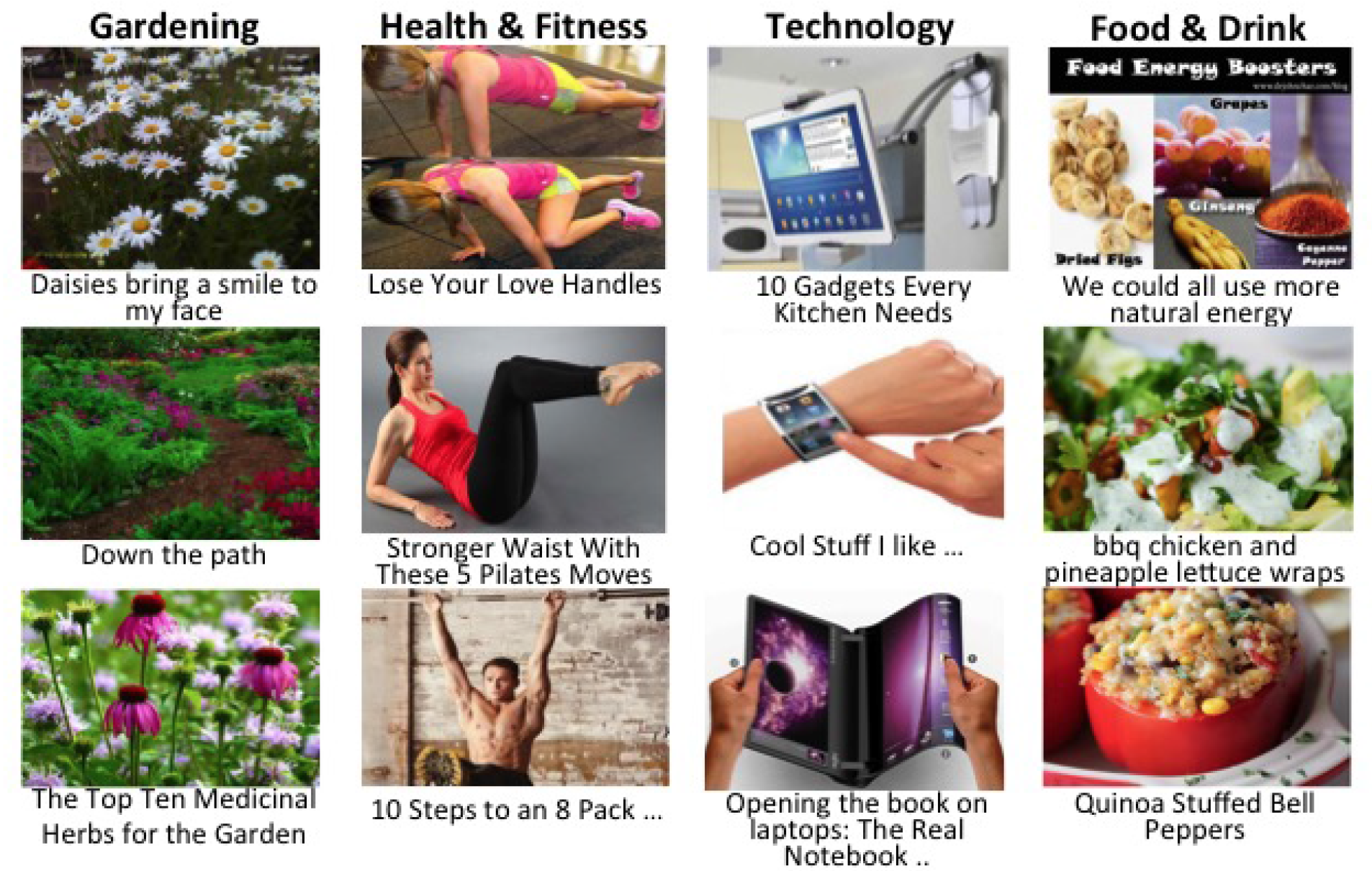
Inferring User Interests on Social Media From Text and Images
We propose to infer user interests on social media where multi-modal data (text, image etc.) exist. We leverage user-generated data from Pinterest.com as a natural expression of users’ interests. Our main contribution is exploiting a multi-modal space composed of images and text. This is a natural approach since humans express their interests with a combination of modalities. We performed experiments using the state-of-the-art image and textual representations, such as convolutional neural …